| Function category | Text functions |
| Volatility | Non-volatile |
| Similar functions | COUNTA |
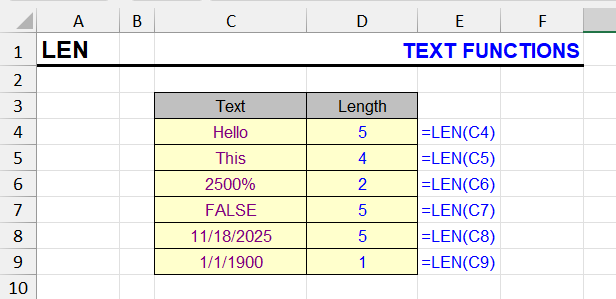
What does the LEN function do?
This function allows you to count the number of characters in a cell, including spaces and numbers, in this string expression. Pay attention to the examples below.
- Although visually 2500% appears as 5 characters, when converted to a text string it’s just 25, so LEN returns 2.
- Dates are converted to whole numbers, where the unit is 01/01/1900 – that’s why the function returns length 1 for it.
There’s one character that the LEN function doesn’t count at all. This is the apostrophe (‘) when it’s at the beginning of a cell. If two apostrophe characters appear consecutively at the beginning of a cell, the second one is counted.
Why does this happen? The reason is that the apostrophe in Excel is one of the special character operators that converts the cell format to text.
LEN function syntax
=LEN(argument)
The function has one argument, which is mandatory. You can specify either a single cell or other calculations using formulas. When used in array functions, the argument can be a range of cells.
LEN – formatting
If the input value is not in text format, it’s converted to text.
Cells in date format are treated as numbers, so they typically contain 5 digits (unless they’re dates close to 1900).
Percentage format is also converted to a natural number, for example, 2500% = 25 (2 characters, see the example table above).
Formula examples, LEN applications
The function is often used as an auxiliary in compound formulas, in combination with other text functions.
These combinations allow solving the most unusual tasks.
Example 1. Count words
How to find out how many words are in an Excel cell? Usually, there’s one more word than spaces between them. If there’s one space, that means two words; if two spaces, then three words, and so on.
If there’s a possibility of more than one space between words, or if there are spaces at the beginning and end of the cell, you can eliminate them using the TRIM function.
You can count spaces in a string by measuring the string length in characters:
- with spaces,
- without spaces,
- and calculating the difference.
How to get a string without spaces? The SUBSTITUTE function will help here.
This is what the formula for cell A1 will look like, taking all these nuances into account. TRIM removes extra spaces, SUBSTITUTE removes them, and LEN measures string lengths:
=LEN(A1) - LEN(SUBSTITUTE(TRIM(A1)," ","")) + 1
Example 2 – count occurrences of a fragment in text
Is there a specific character in the text? And if so, how many?
Let’s consider a couple of formula examples.
Check if a cell has extra spaces
The formula below will check if a cell has extra spaces. This is convenient when you need not just remove spaces, but find out if they were there at all:
=LEN(TRIM(A1))<>LEN(A1)
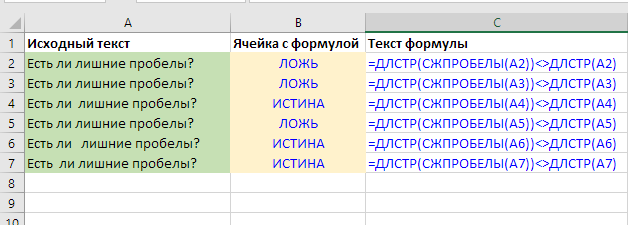
The formula is obvious and quite simple. If the cell length after removing extra spaces with the TRIM function equals the original – that means there are none, and if not equal – there are some.
Note that, although the question itself contains the condition IF, the IF function isn’t needed here. If the equality is true, Excel itself will insert TRUE into the cell, and FALSE if not.
How many times a character or word appears in text
By analogy with the previous example, we can perform not a boolean (YES-NO, TRUE-FALSE) comparison of string lengths before and after removing a character or fragment, but calculate the difference.
If we’re looking for one character, this immediately tells us its frequency.
To remove an arbitrary character from a string, we’ll need the SUBSTITUTE function.
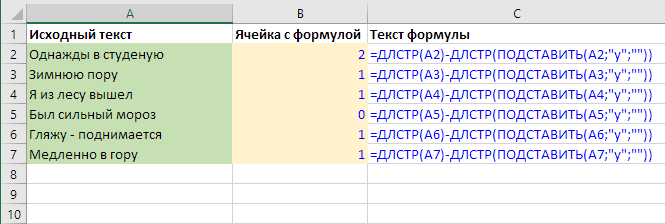
If the text fragment is 2 or more characters long – we also need to divide the result by its length:
=(LEN(A1)-LEN(SUBSTITUTE(A1,B1,"")))/LEN(B1)
In this formula, the source text is in cell A1, and the counted fragment is in cell B1.
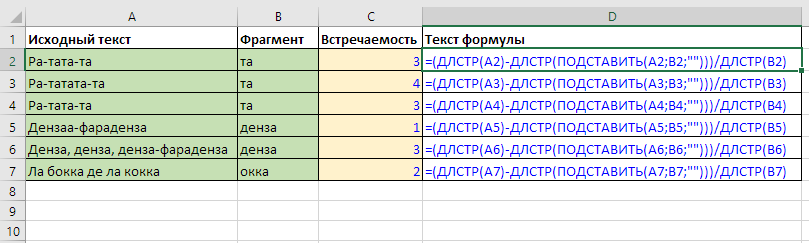
Note rows 5 and 6 – since the “SUBSTITUTE” function is case-sensitive, the first occurrence wasn’t removed from the text. If you need to count occurrences in any case, you might need the LOWER or UPPER functions.
The counted text fragment can be any length.
Another point – the function might not be suitable for counting short words, as one word can be part of another.
Example 3 – extract or remove the last word
Knowing the number of spaces in text, you can replace the last one with a rare character to then calculate its position.
As in the previous example, the SUBSTITUTE function will help us with this – it allows replacing not only all specific text fragments in a string, but also a specific occurrence by order (first, second, etc.).
What does this give us? The last space is nothing but the character separating the last word from the rest of the string. And by its position, we can then remove or extract it with simple manipulations.
The example is discussed in detail here: Remove the last word in Excel
Example 4 – remove first N characters / first word
A simple combination of the RIGHT, SEARCH and LEN functions allows removing the first word from a cell.
The mechanics are simple:
- calculate the position of the first space with the SEARCH function,
- subtract this number from the string length (LEN)
- Extract the resulting difference from the original string with the RIGHT function
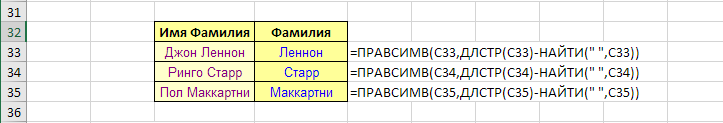
The example is discussed in more detail in the article about the RIGHT function.
If the number of characters is already known in advance, the formula is even simpler – only LEN and RIGHT are needed:
=RIGHT(A1,LEN(A1)-4)
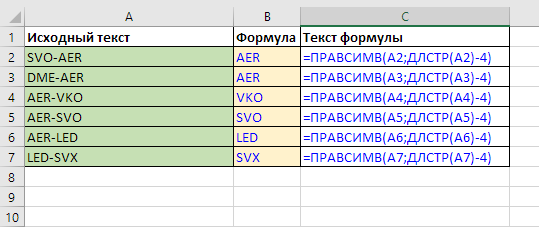
Read more here: remove first N characters in a cell.
Example 5 – last characters of a cell
No matter how obvious it sounds, the position of the last character in a string equals its length in characters. Therefore, knowing the string length, you can, for example:
Below are examples of how to replace the last character in it, taking one character less with LEFT, and concatenation with the desired text using the ampersand:
=LEFT(A1,LEN(A1)-1)&"Text instead of last character"
Or using the REPLACE function, which will take the string length as the position of the character to replace:
=REPLACE(A1,LEN(A1),1,"Text instead of last character")
Example 6 – in array formula
How to count all characters in a range of cells or column?
An array formula based on a combination of the LEN function and the SUM function will help here. The first will create an array of length values for each cell in the range, and the second will sum these values:
={SUM(LEN(RANGE))}
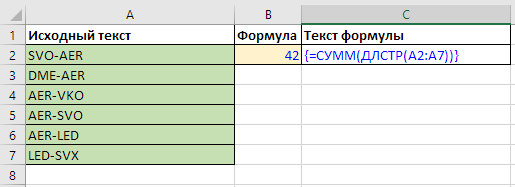
Similarly, using the MAX and MIN functions, you can count the lengths of the longest and shortest strings in a range.
You don't need to type the curly braces; they will appear automatically when entering the array formula with the key combination Ctrl + Shift + Enter (instead of the regular Enter).
Example 7 – extract numbers
The process is discussed in detail in the corresponding article section – how to extract numbers from cells in Excel with a formula.
Other Text functions in Excel
LEFT, RIGHT, MID, TRIM, SUBSTITUTE, REPLACE, FIND, SEARCH, UPPER, LOWER, PROPER
Like the article? Help its author! Buy !SEMTools, it has lots of useful instruments to process text data.