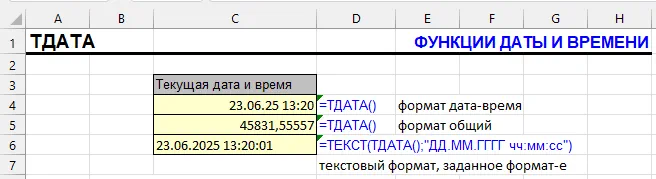
| Function Category | Date and Time |
| Volatility | Volatile |
| Related Functions | TODAY — returns only the current date TEXT — can format date and time as needed DATE, TIME — construct date and time manually |
What Does This Function Do?
The NOW function, despite its name, returns more than just the current date. That’s what the TODAY function does. Our featured function returns both date and time as a single value. No wonder its English name is NOW, which translates to “now”.
Why the function that returns the current date and time wasn’t named “NOW” in Russian remains a mystery.
Like TODAY, the NOW function is volatile — its result updates every time the worksheet changes or recalculates, as well as when the file is opened.
Example return value:
06/17/2025 14:45Used in reports, logs, for timestamping data changes, or in deadline calculations.
Current Date and Time with Millisecond Precision
The NOW function returns the current time with precision up to 10 milliseconds(!). You probably won’t need that, but still :)
To display the current time with such precision, use the TEXT function:
=TEXT(NOW(),"DD.MM.YYYY HH:MM:SS.000")or
=TEXT(NOW(),"DD.MM.YYYY HH:MM:SS,000")depending on whether your Excel settings use a period or comma as the decimal separator.
Formatting
By default, Excel displays both date and time. To show only time or only date, you need to change the cell format.
Example formula to display only time as text:
=TEXT(NOW(),"HH:MM")For date only:
=TEXT(NOW(),"DD.MM.YYYY")Syntax
=NOW()Arguments:
The function takes no arguments. Parentheses are required.
Examples
| Formula | Description | Example Result |
|---|---|---|
=NOW() | Current date and time | 06/17/2025 14:45 |
=TEXT(NOW(),"DD.MM.YYYY HH:MM:SS") | Formatted output | 17.06.2025 14:45:33 |
=NOW()-0.5 | 12 hours ago | 06/16/2025 14:45 |
Features
- The function is volatile, meaning it updates automatically when the workbook is opened and with any data change or event in it, if automatic calculations are enabled in the workbook.
- To fix the value, copy the cell and use paste “as values”.
- The actual result of the function is a number with a fractional part: the integer part is the date, the fractional part is the time.
Other Date and Time Functions in Excel
TIMEVALUE, TIME, YEAR, DATE, DATEVALUE, EDATE, DAY, WEEKDAY, YEARFRAC, EOMONTH, MONTH, MINUTE, WEEKNUM, WORKDAY, DATEDIF, TODAY, SECOND, HOUR, NETWORKDAYS
Like the article? Help its author! Buy !SEMTools, it has lots of useful instruments to process text data.