| Function category | Text functions |
| Volatility | Non-volatile |
| Similar functions | DATEVALUE — converts text to date |
| Similar procedures | Convert numbers stored as text to actual numbers |
What does this function do?
This function converts a piece of text that resembles a number into an actual number.
If the number is in the middle of a long text fragment, it will need to be extracted using other text functions such as SEARCH, MID, FIND, REPLACE, LEFT, RIGHT.
Syntax
=VALUE(text)
Formatting
No special formatting required.
The result will be displayed as a numeric value based on the source text.
If the % sign is included in the text, the result will be a decimal that can then be formatted as a percentage.
If the source text format appears as time hh:mm, the result will be time.
The same applies to other formats.
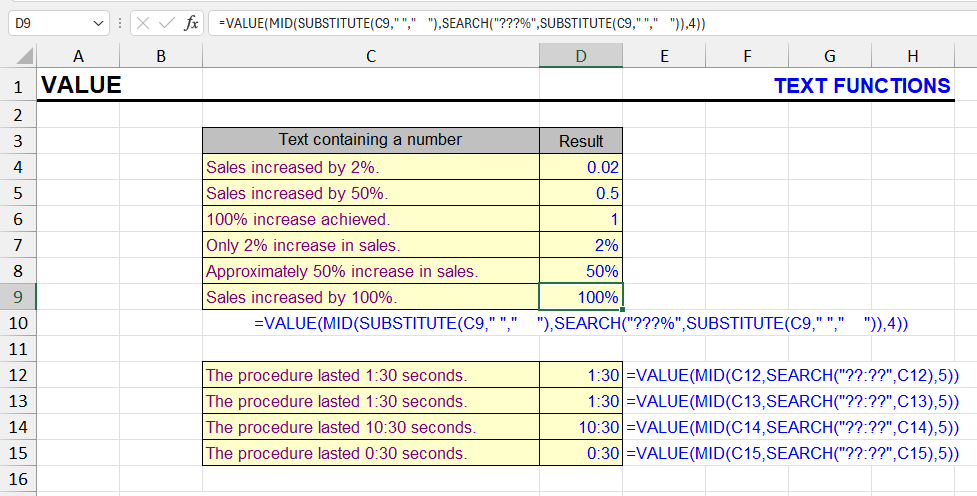
Function usage example
Extracting percentage values from text is difficult without knowing in advance how many digits it contains. This can range from 1 digit (5%) to 4 digits with a decimal (12.25%).
The only way to identify the percentage value is that it always ends with the % sign. It’s impossible to determine the beginning of the value except that it’s preceded by a space.
The main problem is calculating the length of the number to extract it.
If during extraction we assume a maximum length of four digits and the % sign, when the percentage is only one digit, regular extraction using the mask “?????%” will include letters in the expression.
To work around this problem, you can use the SUBSTITUTE function to increase the number of spaces between words in the text. Now when extracting using the mask:
?????%any extra characters will be spaces, which the VALUE function will ignore.
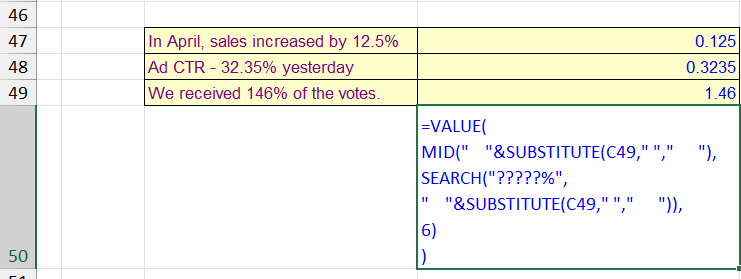
The formula below is similar to the one in the picture and will extract percentages from cell A1 with lengths from 1 to 5 characters, including decimal point:
=VALUE(MID(" "&SUBSTITUTE(A1," "," "),SEARCH("?????%"," "&SUBSTITUTE(A1," "," ")),6))
How the VALUE function helps work with numbers in text
The VALUE function in Excel converts text to numbers when possible. This is especially useful when data is presented as text (e.g., “123”, “005”, “1,000”), but you need to perform arithmetic operations — addition, multiplication, percentage, etc. Without prior conversion, Excel won’t recognize such values as numbers, and the formula result will be incorrect or return an error.
VALUE is often combined with text functions RIGHT, LEFT, MID and SEARCH. This allows you to “cut out” the needed part of a string and then apply mathematical operations to it. This approach is especially relevant when processing codes, SKUs, prices, identifiers that are stored as text.
Useful formulas with VALUE function
1. Round percentages inside a text string:
=TRIM(REPLACE(SUBSTITUTE(A1," ",REPT(" ",10)),MIN(IFERROR(SEARCH(CHAR(ROW(48:57)),SUBSTITUTE(A1," ",REPT(" ",10))),"")),6,TEXT(ROUND(VALUE(MID(SUBSTITUTE(A1," ",REPT(" ",10)),MIN(IFERROR(SEARCH(CHAR(ROW(48:57)),SUBSTITUTE(A1," ",REPT(" ",10))),"")),6)),2),"0%")))For example, the string “81.87% of Russians trust Putin” becomes “82% of Russians trust Putin”.
2. Extract the first number and calculate 20% VAT:
="VAT: "&TEXT(VALUE(MID(SUBSTITUTE(A1," ",REPT(" ",10)),MIN(IFERROR(SEARCH(CHAR(ROW(48:57)),SUBSTITUTE(A1," ",REPT(" ",10))),"")),9)/5,"0")&" rub."
If A1 = “Product cost – 225,500 rub.”, result: VAT: 45100 rub.
3. Add 5 to the number at the beginning of text
For values like “30 cm”.
=TRIM(REPLACE(SUBSTITUTE(A1," ",REPT(" ",2)),1,3,TEXT(VALUE(LEFT(SUBSTITUTE(A1," ",REPT(" ",2)),3))+5,"0")&" "))If A1 = “30 cm”, result: 35 cm
4. Increase the number at the end of text by 15%:
=REPLACE(A1,LEN(A1)-2,3,TEXT(VALUE(RIGHT(A1,3))*1.15,"0"))If A1 = “Amount045”, result: Amount052
Other Text functions in Excel
DATEVALUE, TEXT, LEFT, RIGHT, MID, FIND, SEARCH, REPLACE, SUBSTITUTE, TRIM, LEN
Like the article? Help its author! Buy !SEMTools, it has lots of useful instruments to process text data.